How would you use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate the pH of a buffer solution that is 0.27 M in formic acid (#HCO_2H#) and 0.50 M in sodium formate (HCO_2Na)?
1 Answer
That buffer system has a pH of 4.01
Explanation:
Before I introduce Henderson-Hasselbalch's equation, we should identify the acid and base. Formate
Now, we can use this equation:
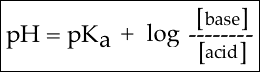
For this type of question we need a pKa, which is not given in your question. Therefore, I Googled the Ka and it is
(
To obtain the pKa from the Ka value, all we have to do is take the
negative logarithm (-log) of the Ka:
Thus, your pKa is 3.74
Next, we can obtain the concentration of base and concentration of acid from the question.
[
We're not really concerned with the sodium cation that attached to the formate ion because it's a spectator ion and it has no effect on the buffer system.
Now, we have all of the information to determine the pH. Let's plug our values into the equation:

