How do biomes differ?
1 Answer
Biomes differ in the amount of precipitation they receive, their temperatures, and the life that inhabits each biome.
Explanation:
Biomes differ in the amount of precipitation they receive, their temperatures, and the life that inhabits each biome.
For example, the types of organisms found in the subtropical desert differ drastically from the organisms found in a tropical rainforest. Each organism is well-adapted to its environment, and a subtropical desert and tropical rainforest are two very different biomes.
If you look at the graph below, you can see that the tropical rainforest has high average temperatures and high precipitation, whereas subtropical deserts have much lower precipitation and great variation in average temperature.
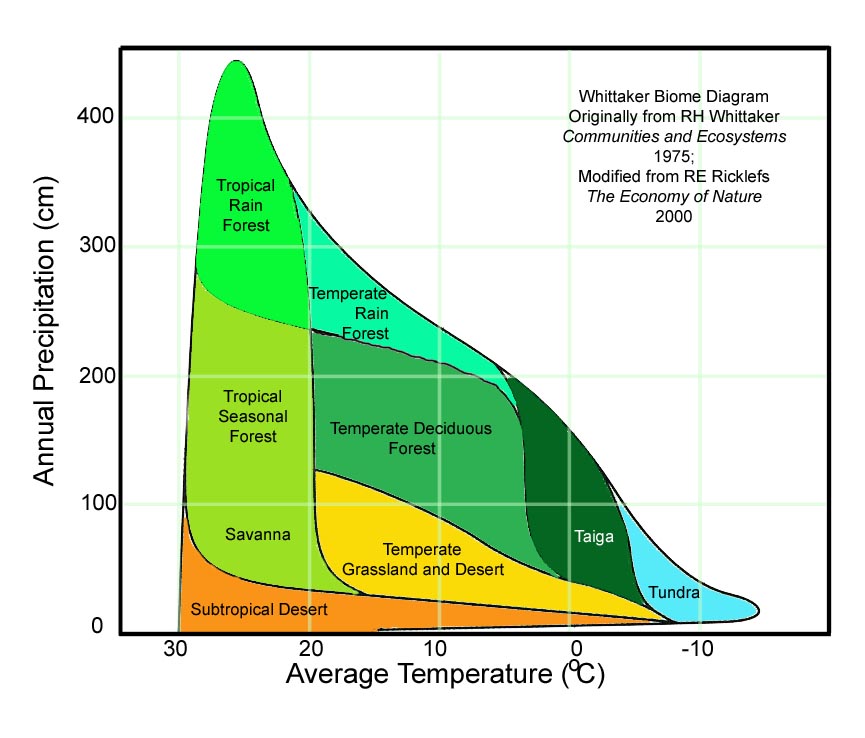
Plants and animals in the desert are well-adapted to low levels of rainfall. Think of cacti which store water for extended periods of time and rodents with kidneys specially designed to absorb as much water as possible.
Plants and animals in the rainforest could not survive in the desert and have their own adaptations to withstand lots of rain. Leaves often have a drip tip to allow water to fall off the leaf quickly. The bark of trees is thinner because losing moisture to evaporation is not a large concern.
Each biome is filled with organisms adapted to live in one of its ecosystems and each biome is determined by temperature and precipitation, accounting for differences between biomes.

