Given the equation N2 + 3F2 --> 2NF3 and the values of deltaH (-264 kJ/mol) and deltaS (-278 J/mol K), what is the standard free energy change for this reaction? B) Use the rxn and table (below) to calculate the average enthalpy of the F-F bond.
bond average bond enthalpy
triple N bond 946
n - f 272
F - F ?
bond average bond enthalpy
triple N bond 946
n - f 272
F - F ?
1 Answer
Explanation:
The relationship you need is:
Average bond enthalpies are usually used to estimate the enthalpy change of a reaction.
In this case we are asked to use the enthalpy change to estimate a bond enthalpy.
Energy needs to be put in to break bonds. Energy is released when new bonds are formed. We can say:
It helps to draw out the structures involved:
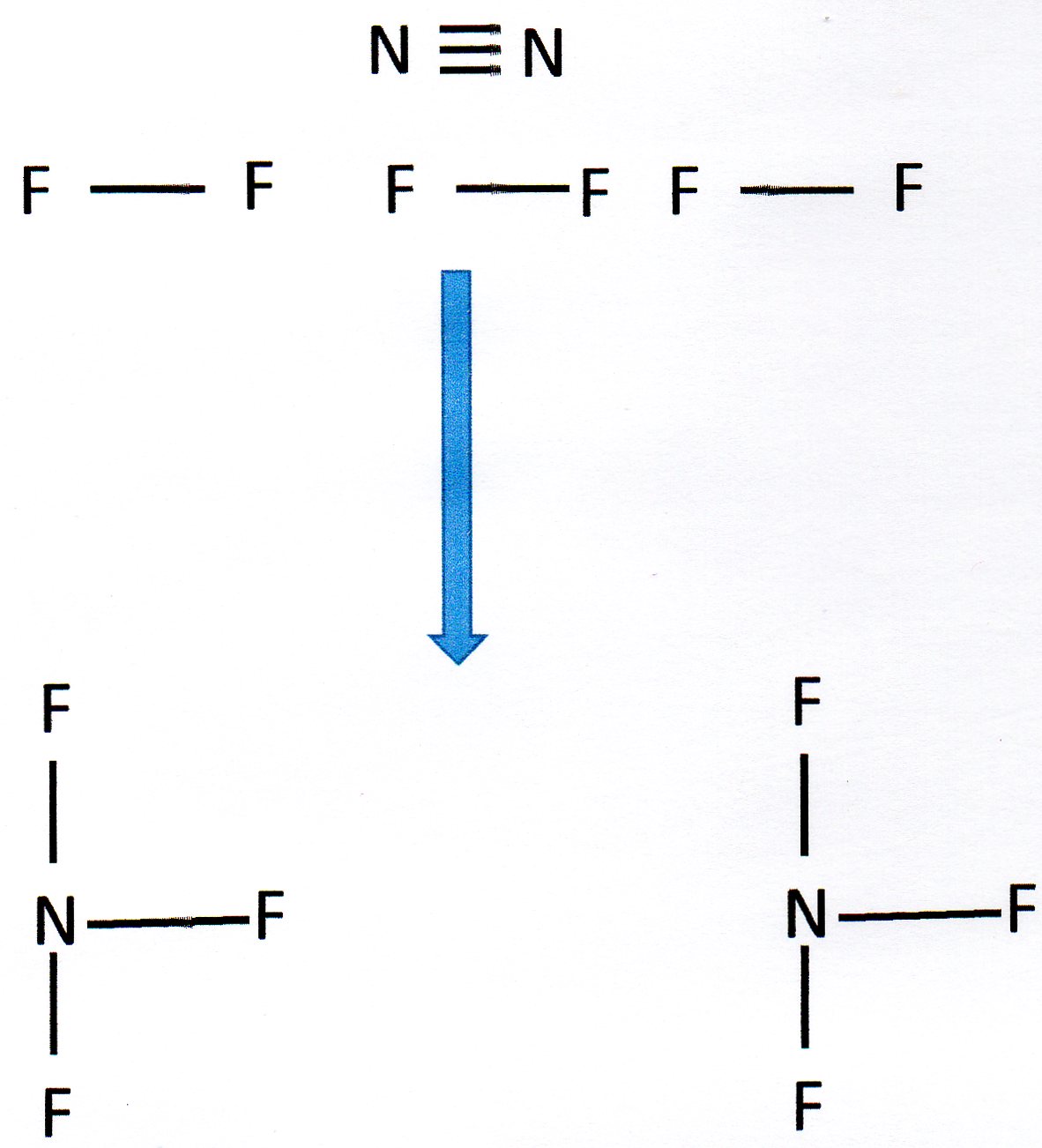
You can see that we need to break 1 N
We then form 6 N - F bonds.
Energy put in =
Energy released =

