A container with a volume of #7 L# contains a gas with a temperature of #420^o C#. If the temperature of the gas changes to #570 ^o K# without any change in pressure, what must the container's new volume be?
1 Answer
The new volume is
Explanation:
Let's start off with identifying our known and unknown variables:
- Initial Volume
- Initial Temperature
- Final Temperature
- Final Volume
We can obtain the answer using Charles' Law which shows that there is a direct relationship between volume and temperature as long as the pressure and number of moles remain unchanged.
The equation we use is
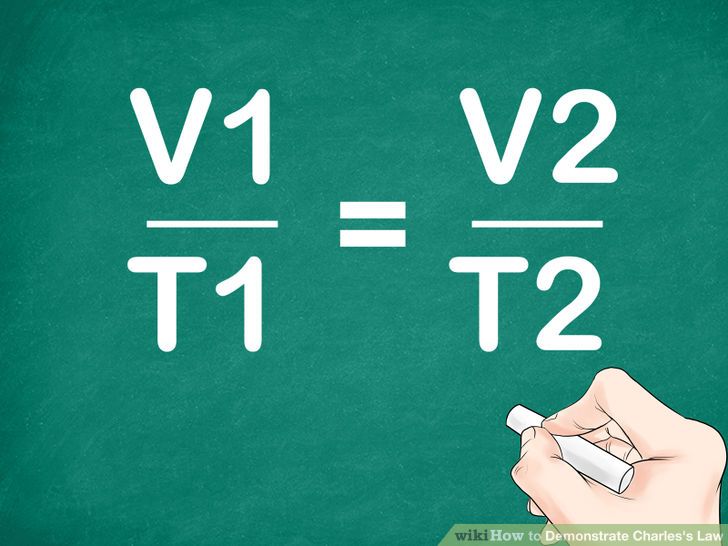
where the numbers
I must also add that the volume must have units of liters and the temperature must have units of Kelvin. In our case the volume is fine, we just have to change the first temperature from centigrade to Kelvins.
We do this by adding
#"273.15K" + 420^@"C" = "693.15K"#
Now we just rearrange the equation and plug and chug.
#V_2 = (T_2 * V_1)/(T_1)#
#V_2 = (570cancel("K") * "7L") / (693.15 cancel("K"))#
#V_2 = "5.76 L"#

