What role does transpiration play in the water cycle?
1 Answer
Transpiration is the evaporation of water from internal surfaces of living parts of plants (leaves, stems, etc.).
Explanation:
In water cycle, plants have critical roles. We know that forest areas guarantee continuation of streamflow due to water regulation in such areas compared to that in open (plant poor) areas.
Transpiration depends on some parameters, such as atmospheric humidity and temperature, area of plant leaves, stems, etc. Opening and closing the stomata is possibly the plant's most important means of regulating water loss via transpiration.
Transpiration accounts for approximately 10% of all evaporating water. Evaporation occurs from streams, lakes, seas, etc. When you think almost 70% of the Earth is covered by seas, you can understand the magnitude of transpiration.
Let me assume that 30% of evaporation occurs from land area. And one-third of this evaporation is called transpiration.
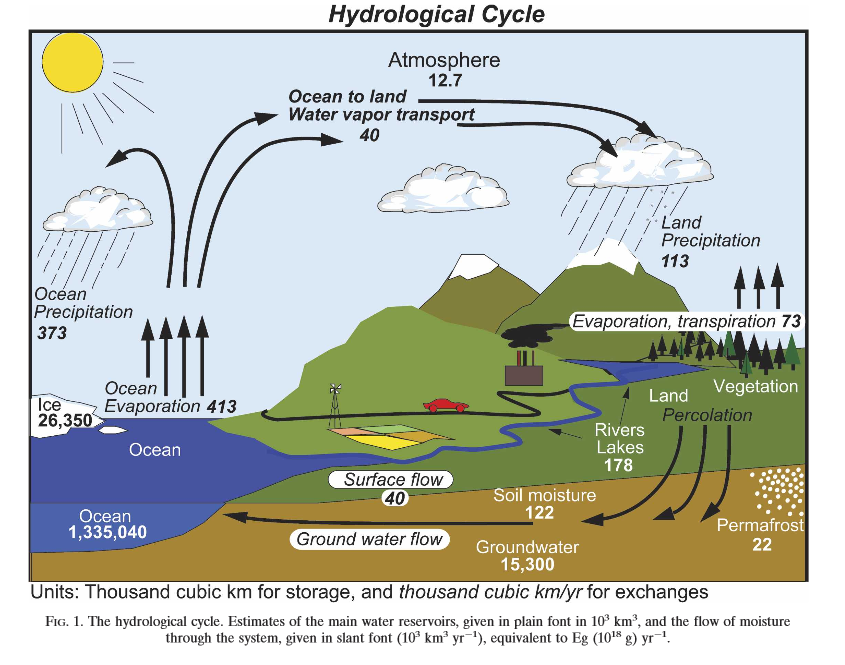
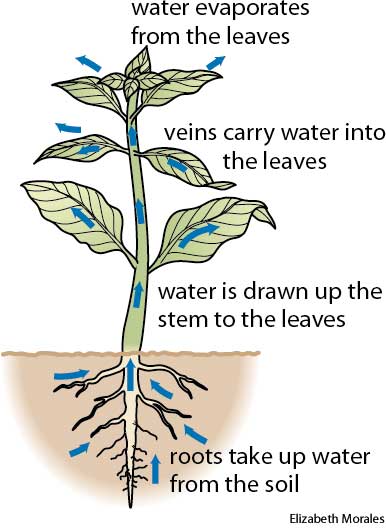
Plants get water via their root system. While they use water (photosynthesis), they also lose this water by transpiration. However, transpiration is a slower (regulated) process compared to that in evaporation from open water bodies. Soil, soil water, plant activity, meteorological parameters, etc. all have roles in transpiration.
Another important feature of plants in water cycle is that they minimize erosion. Rainfall droplets hit the ground with more than 9 meters per second velocity. If it is an open, bare soil, erosion is a big problem. However, rainfall droplets hit plants first and then hit the ground if surface is covered by green plants. Therefore, plant cover minimized erosion rates.



