How do you find the gradient of the curve #y=(3x-9)/(2x^2)# at the point where the curve crosses the #x#-axis?
2 Answers
When the curve crosses the x-axis, the gradient of the curve is
Explanation:
Given-
#y=(3x-9)/(2x^2)#
The curve crosses the x-axis at
Then -
#(3x-9)/(2x^2)=y#
#(3x-9)/(2x^2)=0#
#(3x-9)=0 xx 2x^2#
#3x-9=0#
#3x=9#
#x=9/3=3#
At
The first derivative of the given function gives the gradient of the curve at any point.
#dy/dx=[[(2x^2)(3)]-[(3x-9)(4x)]]/(2x^2)^2#
#dy/dx=[[6x^2]-[12x^2-36x]]/(4x^4)#
#dy/dx=(6x^2-12x^2+36x)/(4x^4)#
#dy/dx=(-6x^2+36x)/(4x^4)#
When the curve crosses the x-axis, the y- coordinate is 0.
At
When the curve crosses the x-axis, the gradient of the curve is
The gradient is
Explanation:
The curve will cross the x-axis as an x-intercept, aka
#0 = (3x - 9)/(2x^2)#
#3x - 9 = 0#
#x = 3#
We now find the derivative.
#y = (3x - 9)/(2x^2)#
#y = 3/(2x) - 9/(2x^2)#
#y = 3/2x^-1 - 9/2x^-2#
#y' = -3/2x^(-2) - 9/2(-2)x^(-3)#
#y'= 9/x^3 - 3/(2x^2)#
The slope of the tangent at that point is
#y'(3) = 9/3^3 - 3/(2(3)^2)#
#y'(3) = 1/3 - 3/(18)#
#y'(3) = 1/3 - 1/6#
#y'(3) = 1/6#
Here is the graph of the function with the tangent at
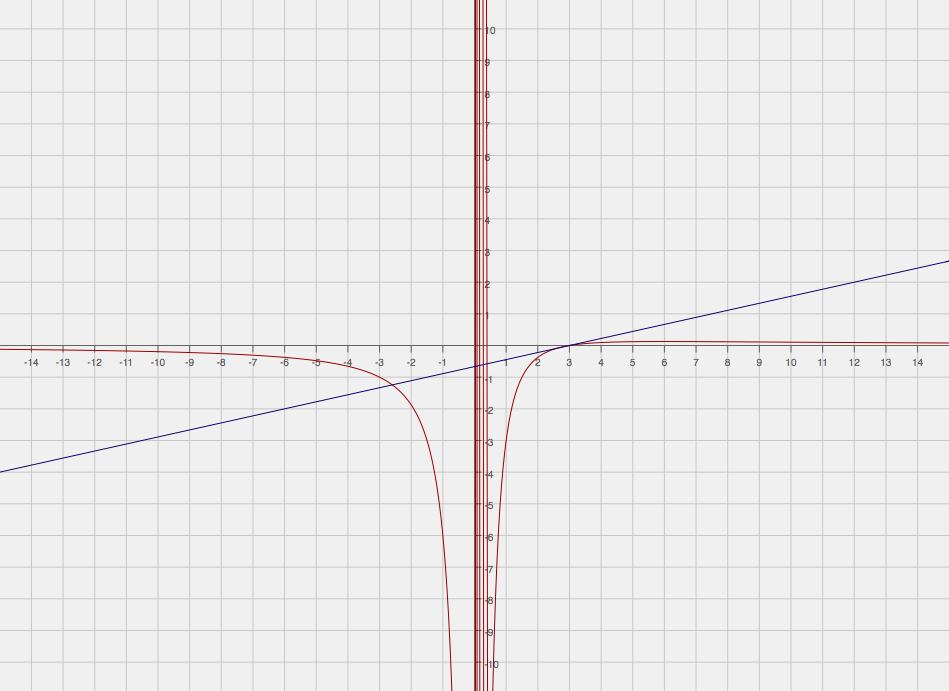
Hopefully this helps!



