Question #f5498
2 Answers
See below.
Explanation:
I don't know if you are working in degrees or radians, so we will do this in degrees. We need to specify an interval to work in, let's make this
We first need to find what angle corresponds to a tangent of
On your calculator there will be a key marked
The angle
We know the the tangent ratio is negative in the II quadrant and the IV quadrant. We have the angle in the IV quadrant now we look for an angle in the II quadrant. If we measure an angle of
This is our second angle. So the two angles in the given interval are:
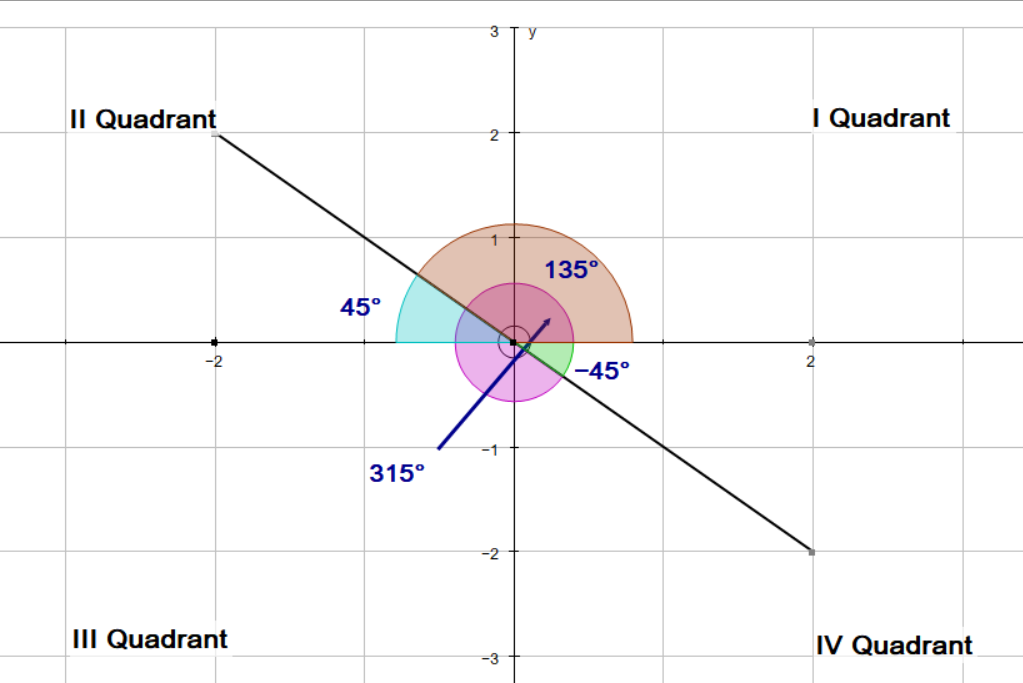
135^@, or (3pi)/4
315^@, or (7pi)/4
Explanation:
There are 2 ways to solve a trig equation: tan t = -1
a. Use the Trig Table of Special Arcs (Angles) and the Unit Circle.
The Trig Table gives -->
tan t = -1 -->
The unit circle gives another t that has the same tan value (-1) -->
b. Use calculator and unit circle.
tan t = - 1
Calculator gives
Unit circle gives another


