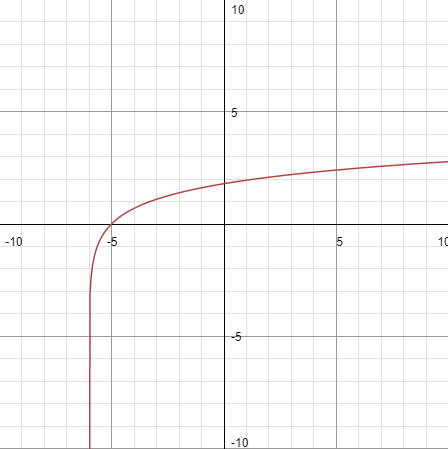
#h(x) = ln(x+6)# , #x>##-6#
#Dh=(-6,+oo)#
#h'(x)=1/(x+6)##(x+6)'##=1/(x+6)# #>0#, #x> -6#
So that means that #h# is strictly increasing ↑ in #(-6,+oo)#
#h# is obviously continuous in #(-6,+oo)# as composition of #h_1#(x)=x+6 & #h_2#(x) = #lnx#
#h(Dh)=h(#(-6,+oo)#)#= (#lim_(xrarr-6)h(x)#,#lim_(xrarr+oo)h(x))# #=(-oo,+oo)##=R#
because #⋅##lim_(xrarr-6)h(x)#= #lim_(xrarr-6)ln(x+6)#
#x+6=y#
#xrarr-6#
#yrarr0#
#= lim_(yrarr0)lny# #=-oo#
#⋅##lim_(xrarr+oo)h(x)#=#lim_(xrarr+oo)ln(x+6)##=+oo#
Note: you can also show this using the reverse #h^-1# function. (#y=ln(x+6)=>......)#