Radiation from the sun often gets trapped in the earth's atmosphere. What is the reason for this?
2 Answers
see below
Explanation:
electromagnetic radiation hitting the matter interact with it accordind with the chemical bonds of the molecules hitted . This bonds pass from a foundamental state to an excitated state, assorbing the radiations, and to do this passage need a fixed energy that is given only by a certain elecrtomagnetica radiation characterized by a specific wavelength.
So, for example
The stratosferic
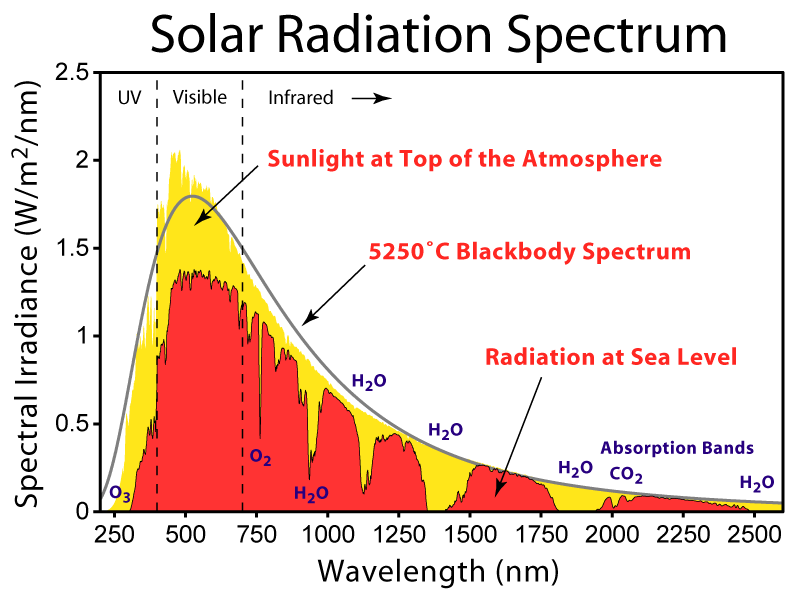
Greenhouse gases.
Explanation:
Greenhouse gases are gases that allow radiation of 0.5 micron wavelength to free pass through but block radiation around 10 microns.
http://www.oocities.org/marie.mitchell@rogers.com/GreenhouseEffect.html
The charts above show for various gases, what radiation wavelength is absorbed by that gas. The absorption is shown in green (except the bottom chart). The wavelength between the 2 red lines is the main wavelength for radiation from the sun. This is also known as visible light. You will see that there is almost zero absorption by any of the gases of this wavelength. Therefore the radiation passes through freely.
If you look at the absorption above 1 micron you will see quite a bit of absorption at various wavelengths. These wavelengths are called infrared but more importantly sensible heat. That is heat you can feel.
What makes this important is that when visible light hits the surface of the Earth, it is absorbed and there is an increase in energy of the Earth. This energy is released at longer wavelengths, generally speaking as heat.
So in summary, solar radiation is not absorbed by the atmosphere but when it is transformed into terrestrial radiation it is absorbed (or trapped if you prefer).
