Question #3ec9c
1 Answer
The potassium ion is the "best fit" to make the most stable complex.
Explanation:
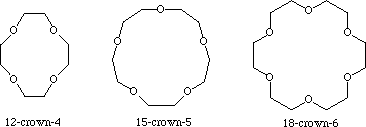
Crown ethers
The most common crown ethers are cyclic oligomers formed from repeating
Of these, the most common ones are [12]-crown-4, [15] crown-5, and
[18]-crown-6.
These ethers have a "hole" or cavity in the middle, with the
Thus the hole is surrounded by a negative charge density.
This means that metal ions will be attracted to the hole.
Formation constants
As the ionic size of the metal increases, the formation constants increase and then fall off.
I would guess that there is an "ideal" ionic size for the ion to fit the hole and get maximum stabilization: small ions are too small and large ions are too large.
However,
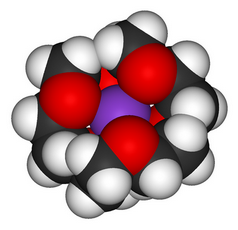
(From Wikimedia Commons)
Confirmatory evidence
Small crown ethers preferentially complex small ions, and large crown ethers preferentially complex large ions.
Here are the pairings
The larger rings have more flexibility and can adjust their cavity size to match that of the cation.