What is the equilibrium constant of pure water at 25°C?
1 Answer
Explanation:
Sometimes, in pure water, one proton (
This causes the
This process is called the auto-ionization or self-ionization of water, since
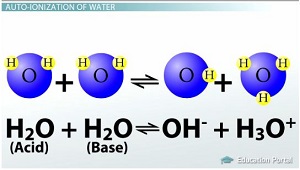 Study.com
Study.com
So, this reaction will sometimes occur:
However, it's important to note that this reaction only happens very rarely. As such, the equilibrium constant, which is a measure of the concentration of products to the concentration of reactants, will be very low.
In fact, at

