#" "#
The function:
#color(red)(f(x)=(2x^2-5x+2)/(2x^2-x-6)# Eqn.1 is rational.
#color(green)("Step 1:"#
Set #DR = 0#
#rArr 2x^2-x-6=0#
Factorize:
#rArr 2x^2+3x-4x-6=0#
#rArr x(2x+3)-2(2x+3)=0#
#rArr (2x+3)(x-2)=0#
Factors of #color(blue)(DR = (2x+3)(x-2)# Res.1
#color(green)("Step 2:"#
Set #NR = 0#
#rArr 2x^2-5x+2=0#
Factorize:
#rArr 2x^2-x-4x+2=0#
#rArr x(2x-1)-2(2x-1)=0#
#rArr (2x-1)(x-2)=0#
Hence, the factors of #color(blue)(NR = (2x-1)(x-2)# Res.2
#color(green)("Step 3:"#
Using the Res.1 and Res.2
Eqn.1 can now be rewritten as
#color(blue)(f(x)= [(2x-1)(x-2)]/[(2x+3)(x-2)]# Eqn.2
#color(blue)(f(x)= [(2x-1)cancel((x-2))]/[(2x+3) cancel((x-2)]#
#color(blue)(f(x)=(2x-1)/(2x+3)# Eqn.3
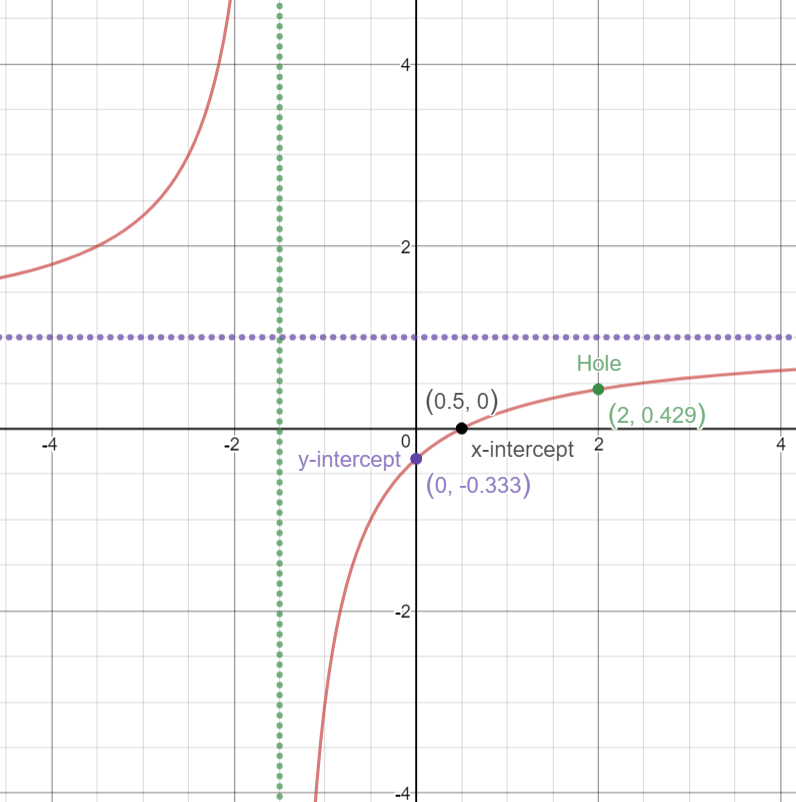
#color(green)("Step 4:"# Horizontal Asymptote
Refer to Eqn.1:
The leading coefficients of the highest terms are #color(red)(2, 2#
#rArr 2/2=1#
Horizontal Asymptote is at #color(blue)(y=1#
#color(green)("Step 5:"# Vertical Asymptote
Consider DR
#rArr 2x+3#
#rArr 2x=-3#
#rArr x=(-3/2)#
Vertical Asymptote is at #color(blue)(x=(-3/2)#
#color(green)("Step 6:"# Hole
Consider Eqn.2
#color(blue)(f(x)= [(2x-1)(x-2)]/[(2x+3)(x-2)]#
#color(blue)((x-2)# is the common factor,
Set #color(blue)((x-2)=0#
#color(blue)(x=2)#
y-coordinate value of the hole
#color(blue)(f(x)=(2x-1)/(2x+3)# Eqn.3
Substitute #color(red)(x=2#
#rArr (2*2 - 1)/(2*2+3#
#rArr 3/7#
Hence, the hole is at #color(blue)((2, 3/7)#
#color(green)("Step 7:"# x-intercept
Set #color(blue)(2x-1=0#
#rArr 2x=1#
#rArr x = 1/2#
Hence, the x-intercept is at #color(blue)((1/2, 0)#
#color(green)("Step 8:"# y-intercept
Consider: #y=(2x-1)/(2x+3)#
Substitute #color(red)(x=0#
#rArr (2*0-1)/(2*0+3)=-1/3#
y-intercept is at #color(red)((0, -1/3)#
#color(green)("Step 9:"# Graph