What is the difference between a longitudinal wave and a transverse wave?
2 Answers
See below
Explanation:
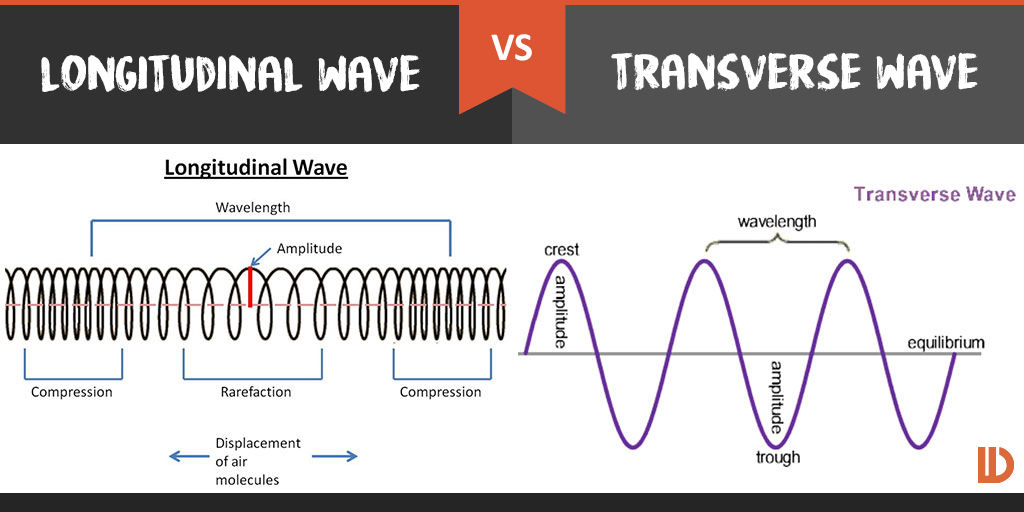
In a longitudinal wave, the propagation of energy is in the direction of the motion, while in a transverse wave the propagation of energy is perpendicular to the direction of motion.
See answer below
Explanation:
Given: Difference between a longitudinal wave and a transverse wave
First let's define the two types of waves:
A longitudinal wave is a wave that moves in the direction that it was started. It has a compression (increased intensity) of the medium particles and a rarefaction (a reduction of intensity). A slinky lying horizontal and pushed horizontally is a simple way to demonstrate a longitudinal wave.
A typical example is a longitudinal wave is a sound wave. Another example is a shock wave.
A transverse wave is wave that travels perpendicular or at right angles to the direction it was started. A string or slinky moving up and down (one end being held stationary and the other moving up and down) is is a simple way to demonstrate a transverse wave.
An example of transverse waves are a string on a guitar vibrating, or ripples on the surface of water.
Differences:
-
Movement: The movement of the medium is different. In the longitudinal wave, the medium moves left to right, while in thee transverse wave, the medium moves vertically up and down.
-
Longitudinal waves have a compression and rarefaction, while the transverse wave has a crest and a trough.
-
Longitudinal waves have a pressure variation, transverse waves don't.
-
Longitudinal waves can be propagated in solids, liquids and gases, transverse waves can only be propagated in solids and on the surfaces of liquids.
-
Longitudinal waves have a change in density throughout the medium, transverse waves don't.