Question #54401
1 Answer
Antibiotics are ineffective in treating viral diseases because they are designed to disrupt activities that don't even take place in a virus.
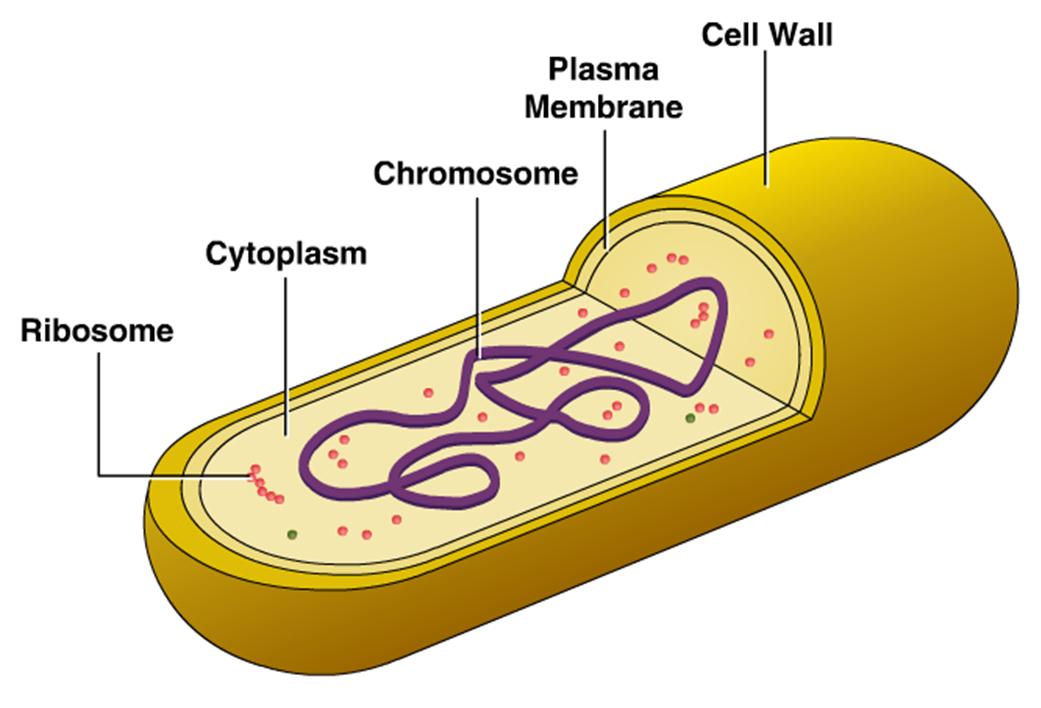
A bacterium is essentially a cell with machinery inside for making DNA and proteins.
An antibiotic works either by disrupting the building of the cell wall or the processes that take place inside the cell.
A virus is not a cell. It is basically just a protein coating with DNA or RNA inside it.

Antibiotics are designed to disrupt activities that don't even take place in a virus, so they have no effect on it.
A virus reprograms its host's cells to make new viruses, and almost all the proteins used in this process are normal parts of the body.
An antiviral drug must target just the few proteins of the virus and not the normal proteins of the cell.

