(1) T/F Do all lipids have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail? (2) How is a rate constant related to the Gibbs' free energy of activation, DeltaG^‡?
1 Answer
1) Lipids may mean fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, certain glycerides, phospholipids, and more.
As such, only some lipids have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail (a phospholipid, for example). All literally means all, without exception.
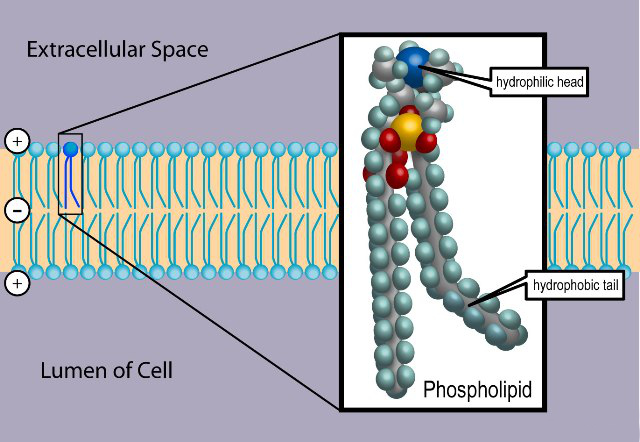
A phospholipid looks like this:
 https://upload.wikimedia.org/
https://upload.wikimedia.org/
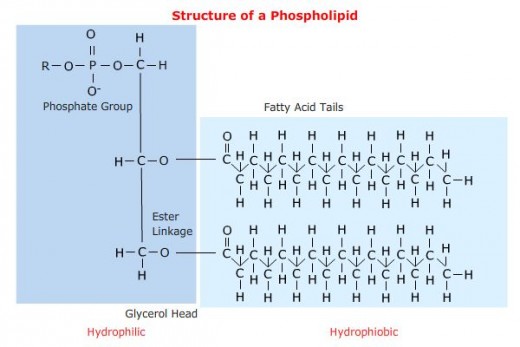
The head group is made up of a phosphate and some other component, while the tail is basically a derivative of a two-tailed fatty acid (a carboxylic acid with a long alkyl tail).
 http://usercontent1.hubimg.com/
http://usercontent1.hubimg.com/
But again, not all lipids have this characteristic. Some are simply hydrophobic but not hydrophilic.
2) The rate constant
\mathbf(k prop e^(-color(green)(DeltaG^‡)"/"RT))
http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/
...kind of like how it is proportional to the activation energy of the reaction:
\mathbf(k = Ae^(-color(green)(E_a)"/"RT))
 https://upload.wikimedia.org/
https://upload.wikimedia.org/
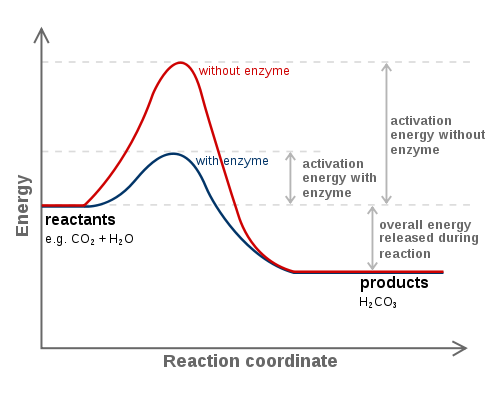
Catalysts actually tend to somehow alter the mechanism of the reaction to lower the activation energy, making a reaction kinetically favorable.
A common way to do this is to stabilize the transition state. Enzymes are frequently said to alter
If you increase
A higher rate constant thus results, which makes sense because a catalyst is supposed to speed up a reaction. A higher

