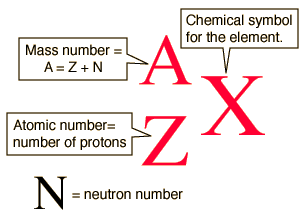A certain element is radioactive. It emits alpha particles. Each of its nuclei contains 92 protons and 142 neutrons. Write a nuclear equation that describes the change that takes place by alpha emission?
1 Answer
Explanation:
The first thing to do here is make sure that you have a clear understanding of what an alpha particle is.
An alpha particles is simply the nucleus of a helium-4 atom,
Now, your next goal here is to figure out the mass number of the radioactive isotope given to you by the problem.
As you know, the mass number,
#color(blue)(|bar(ul(color(white)(a/a)A = Z + Ncolor(white)(a/a)|)))#
In your case, you have
#A = "92 protons" + "142 neutrons" = 234#
Next, use isotope notation to write the isotopic symbol for this element
A quick look in the periodic table will reveal that your unknown element is uranium,
Now, when a nuclide emits an alpha particle, two things happen
- its atomic number decreases by
#2# because an lpha particle contains#2# protons- its mass number decreases by
#4# because an alpha particle contains#2# protons and#2# neutrons
You can thus set up your nuclear equation like this
#""_ (color(white)(a)92)^234"U" -> ""_m^n"X" + ""_2^4alpha#
In any nuclear reaction, charge and mass are conserved, which means that you can write
#92 = m + 2 " "->" "# conservation of charge
#234 = n + 4 " "->" "# conservation of mass
You will thus have
#m = 92 - 2 = 90" "# and#" "n = 234 - 4 = 230#
Another quick look in the periodic table will reveal that the element that has
The balanced nuclear equation will thus be
#color(green)(|bar(ul(color(white)(a/a)color(black)(""_ (color(white)(a)92)^234"U" " "->" " ""_ (color(white)(a)90)^230"Th" " "+" " ""_2^4alpha)color(white)(a/a)|)))#