Question #58548
1 Answer
Mitose is the process in which a cell divides into two identical new daughter cells.
Explanation:
Mitosis consists of multiple processes to in the end create 2 identical new cells. The process of mitosis is showed in the picture below.
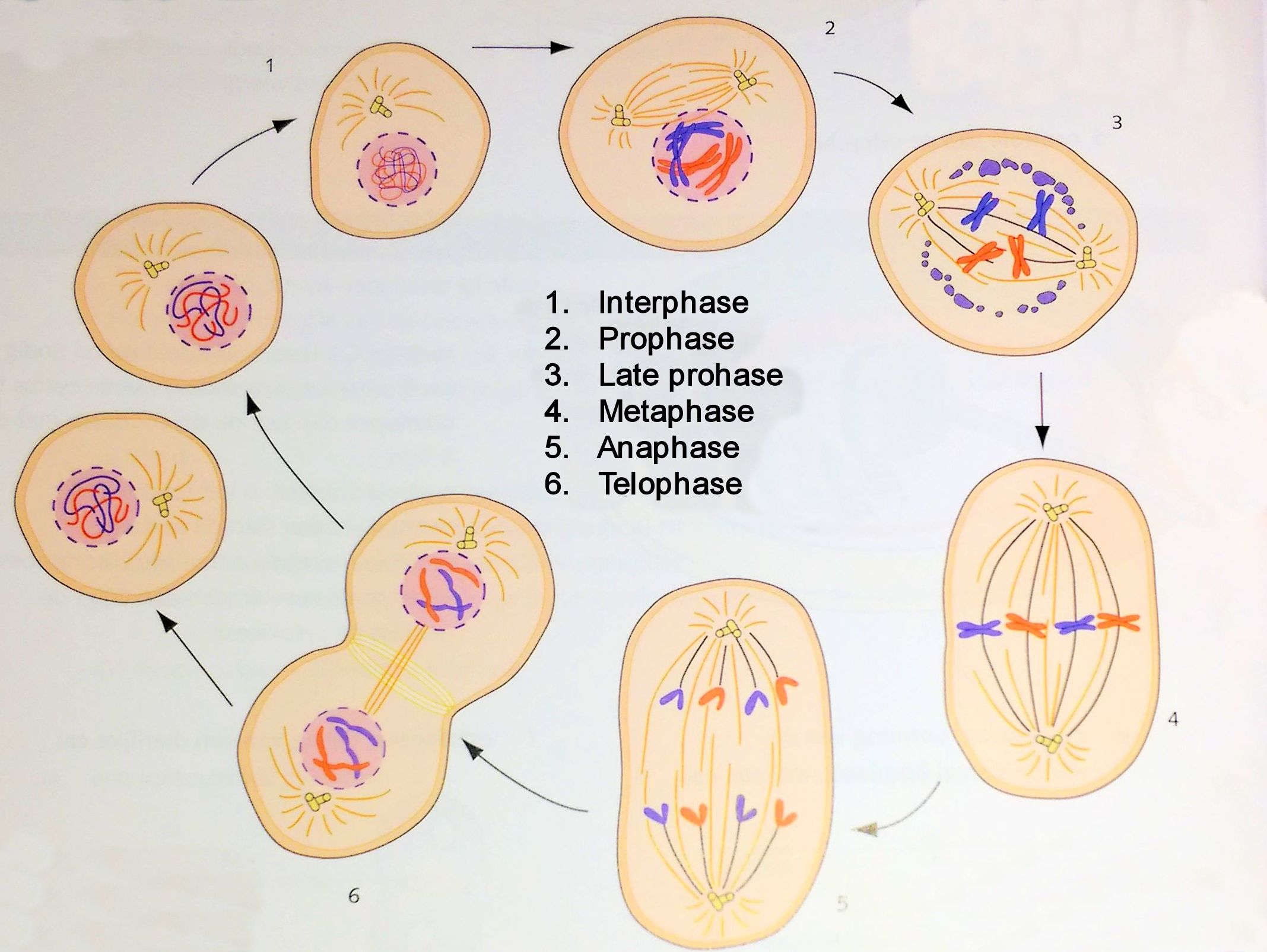
In this cycle, we have the interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and the telophase.
The interphase is the time between two cell division. In this phase, the cell is at rest and does not divide. The interphase is the longest phase of the cycle and consists of the
After the interphase, the cell is ready to undergo mitosis. In the interphase, the chromosomes are not visible.
In this phase, the cell prepares for cell division. The nuclear envelope is dissolved and the chromosomes will be tightly packed while moving to the middle of the cell. In this phase, some microtubules will be attached already to the chromosomes. When the nuclear envelope is dissolved, we speak of the prometaphase or the late prophase. The chromosomes are visible will become visible yet.
In this phase, the chromosomes that are attached to the microtubules will meet in the metaphase plate. which is in the middle of the cell between the two centromeres. The dark spot in the picture below are the tightly packed chromosomes.
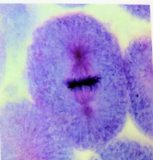
In the anaphase, the chromatids will move towards the centromeres at the two sides of the cell. The purple spots in the picture below are the chromatids that are moving away from each other in the direction of the centromeres (middle of the pink spots).
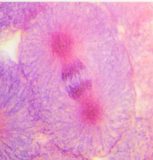
In this phase, two new nuclear envelopes will be formed to 'catch' the chromatids. Also, a new cell membrane is produced to separate the two new daughter cells by a phase called cytokinesis.
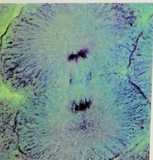
Thanks to mitosis, the growth and development of organisms are possible. In the cell cycle, mistakes can be made. For example, the microtubules will attach to a wrong part of the chromatids, causing a non-equal separation.
The cells have control points in which they investigate if there are any mistakes occurred. The cell can then take action by, for example, killing itself in a process called apoptosis. More about cell cycle regulation can be found here.
(Source pictures: "Grote spectrum encycopedie 1975")
