An object with a mass of 8 kg8kg is on a plane with an incline of - pi/3 −π3. If it takes 9 N9N to start pushing the object down the plane and 7 N7N to keep pushing it, what are the coefficients of static and kinetic friction?
1 Answer
If angle of inclination is
mu_s = 0.710μs=0.710
mu_k = 0.680μk=0.680
See explanation regarding angle.
Explanation:
We're asked to find the coefficient of static friction
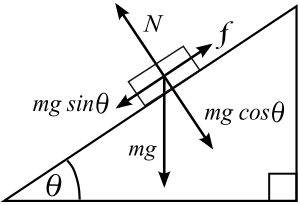 upload.wikimedia.org
upload.wikimedia.org
We'll call the positive
There is no net vertical force, so we'll look at the horizontal forces (we WILL use the normal force magnitude
We're given that the object's mass is
Since the angle is
-(pi)/3−π3 , this would be the angle going down the incline (the topmost angle in the image above). Therefore, the actual angle of inclination is
pi/2 - (pi)/3 = ul((pi)/6
The formula for the coefficient of static friction
f_s <= mu_sn
Since the object in this problem "breaks loose" and the static friction eventually gives way, this equation is simply
color(green)(ul(f_s = mu_sn
Since the two vertical quantities
n = mgcostheta = (8color(white)(l)"kg")(9.81color(white)(l)"m/s"^2)cos(pi/6) = color(orange)(ul(68.0color(white)(l)"N"
Since
color(green)(f_s) = mgsintheta + 9 "N"
= (8color(white)(l)"kg")(9.81color(white)(l)"m/s"^2)sin(pi/6) + 9color(white)(l)"N" = color(green)(48.2color(white)(l)"N"
The coefficient of static friction is thus
mu_s = (f_s)/n = (color(green)(48.2)cancel(color(green)("N")))/(color(orange)(68.0)cancel(color(orange)("N"))) = color(red)(ulbar(|stackrel(" ")(" " 0.710" ")|
The coefficient of kinetic friction
color(purple)(ul(f_k = mu_kn
It takes
color(purple)(f_k) = mgsintheta + 7 "N"
= 39.2color(white)(l)"N" + 7 "N" = color(purple)(46.2color(white)(l)"N"
The coefficient of kinetic friction is thus
mu_k = (f_k)/n = (color(purple)(46.2)cancel(color(purple)("N")))/(color(orange)(68.0)cancel(color(orange)("N"))) = color(blue)(ulbar(|stackrel(" ")(" " 0.680" ")|
