How do you find the horizontal and vertical tangents to x = Cos(3t) and y = 2sin(t)?
2 Answers
Recall that
(dy/(dt))/(dx/(dt)) = dy/dx
Therefore
dy/dx = (2cost)/(-3sin(3t))
Horizontal tangents occur when the derivative equals
0 = 2cost -> t = pi/2 + pin
Vertical tangents occur when the derivative is undefined.
-3sin(3t) =0 -> 3t = pin -> t = pi/3n
Hopefully this helps!
Horizontal Tangents occur when
Vertical Tangents occur when
Explanation:
We have the following parametric equation:
x = cos(3t) ... [A]
y =2sin(t) ... [B]
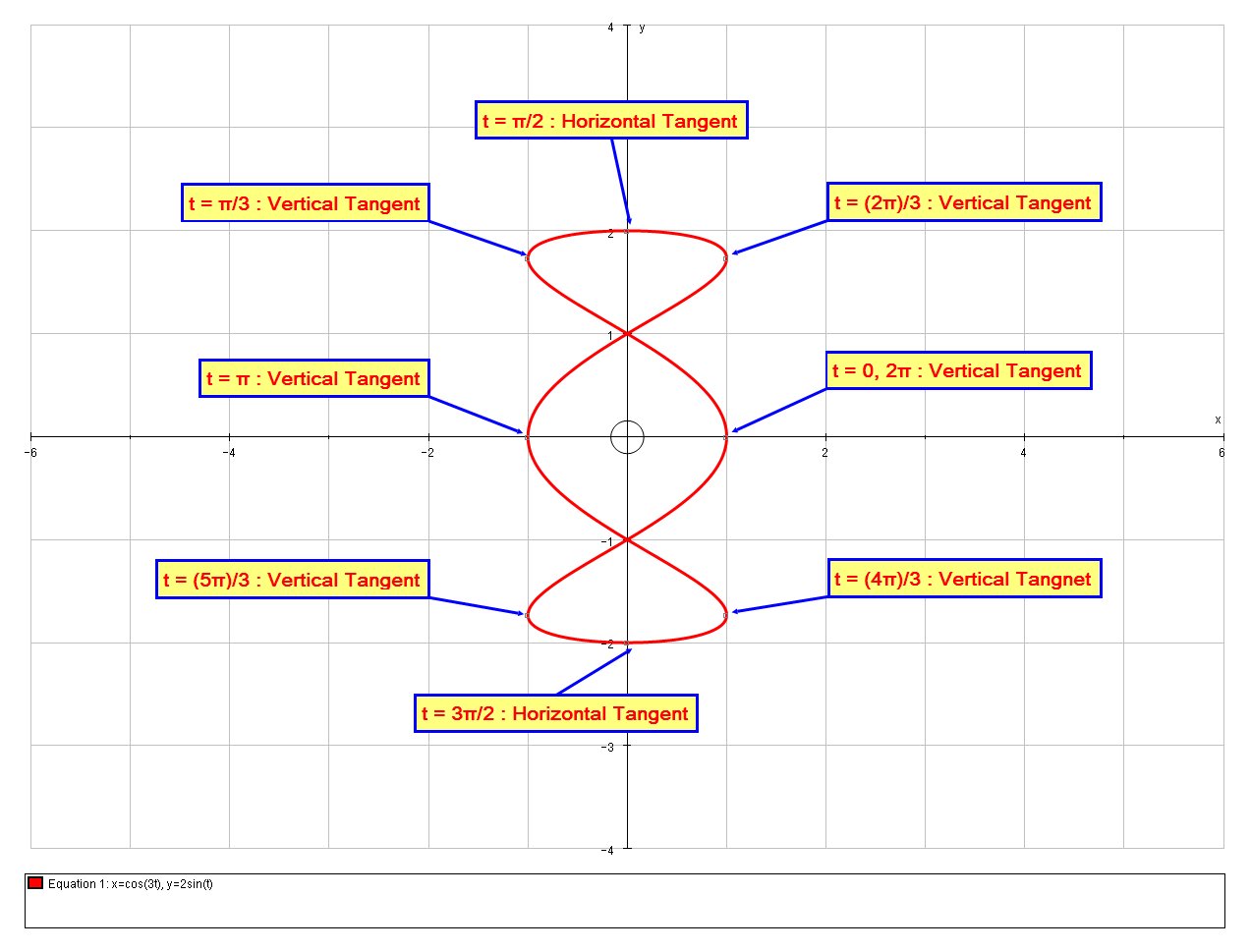
The entire curve is mapped out for
Horizontal tangents occurs when
dy/dx = (dy//dt) /(dx//dt)
Horizontal Tangents:
Differentiating [B] wrt
t we get:
dy/dt = 2cost
dy/dt = 0 => 2cost = 0
:. cost=0 => t = pi/2, (3pi)/2 \ " for " \ t in [0,2pi]
Vertical Tangents:
Differentiating [A] wrt
t we get:
dx/dt = -3sin(3t)
dx/dt = 0 => -3sin(3t) = 0
:. sin(3t)=0 => 3t = 0, pi, 2pi, 3pi, 4pi, 5pi, 6pi \ " for " \ 3t in [0,6pi]
:. t = 0, pi/3, (2pi)/3, pi, (4pi)/3, (5pi)/3, 2pi \ " for " \ t in [0,2pi]
The last value of