Let us solve the following rational inequality.
f(x)={x+1}/{x^2+x-6} le 0
Set the numerator equal to zero, and solve for x.
x+1=0 => x=-1
(Note: f(-1)=0)
Set the denominator equal to zero, and solve for x.
x^2+x-6=(x+3)(x-2)=0 => x=-3,2
(Note: f(-3) and f(2) are undefined.)
Using x=-3,-1,2 above to split the number line into open intervals:
(-infty,-3), (-3,-1),(-1,2), and (2,infty)
Using sample numbers x=-4,-2,0,3 for each interval above, respectively, we can determine the sign of (LHS).
f(-4)=-2<0 => f(x)<0 on (-infty,-3)
f(-2)=1/4>0 => f(x)>0 on (-3,-1)
f(0)=-1/6<0 => f(x)<0 on (-1,2)
f(3)=2/3>0 => f(x)>0 on (2,infty)
Hence, f(x) le 0 on (-infty,-3)cup[-1,2).
(Note: -1 is included since f(-1)=0.)
The graph of y=f(x) looks like:
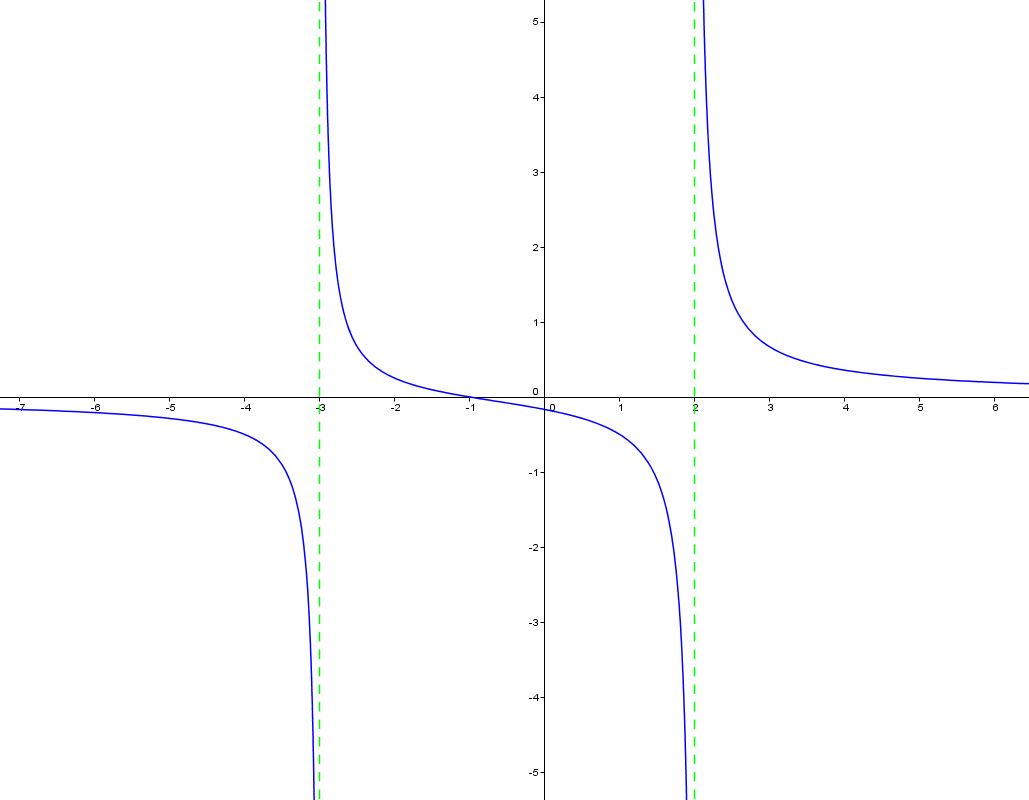
I hope that this was helpful.

