How does one tell if a compound is optically active or inactive by looking at it? For examples: 1-4-dichloro-2-methylpentane and 1,2-dichloro-2-methylpentane
1 Answer
Mar 8, 2016
You look for a chiral carbon — a carbon atom that has four different groups attached.
Explanation:
1,4-Dichloro-2-methylpentane
The structure of 1,4-dichloro-2-methylpentane is
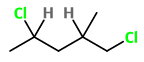
You see that
The 4 groups attached to
The 4 groups attached to
The compound has two chiral carbons, so it will be optically active.
1,2-Dichloro-2-methylpentane
The structure of 1,2-dichloro-2-methylpentane is
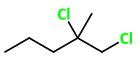
Here,
The 4 groups attached to
The compound has a chiral carbon, so it will be optically active.

