How does the metal activity series relate to single displacement reactions?
1 Answer
A metal that is attached to one lower in the activity series will corrode preferentially and protect the less reactive metal.
You can read about the metal activity series at
http://socratic.org/questions/what-are-metal-activity-series
Corrosion is the electrochemical oxidation of a metal in the presence of water and oxygen. An example is the rusting of iron.
During corrosion, the iron is oxidized to Fe²⁺ ions.
Fe(s) → Fe²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻
The Fe²⁺ ions react with OH⁻ ions to form solid Fe(OH)₂. This oxidizes further and dehydrates to form rust.
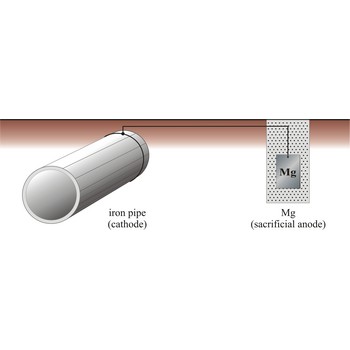
If we supply electrons to the iron by connecting it to a more reactive metal such as zinc or magnesium, the iron will not rust.
This is called sacrificial protection, because the more reactive metal corrodes preferentially, leaving the iron intact.
 c2.staticflickr.com
c2.staticflickr.com
In the above picture, a strip of zinc sacrificially protects a steel rudder from corrosion.
In the same way, bags of magnesium scrap are attached at intervals to underground pipelines to prevent the pipe from corroding.
 glossary.periodni.com
glossary.periodni.com

