Question #8fe6e
1 Answer
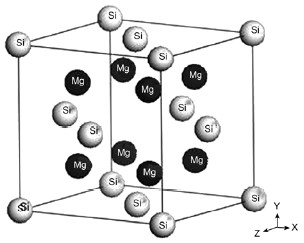
Magnesium silicide, or
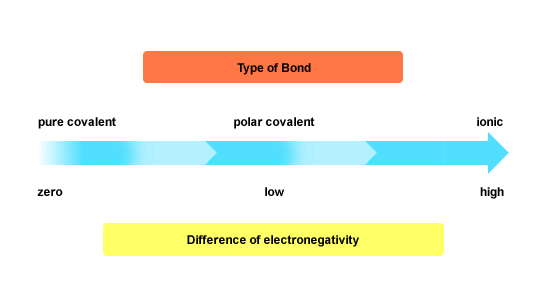
The difference in electronegativity between magnesium and silicon is about 0.6, which is very close to the 0.5 value set as threshold for covalent bonding.
This is why the bond is considered to be polar covalent. You can think of the difference in electronegativity as an indicator of what predominant character a bond between two atoms will have
As a powder, magnesium silicide crystalizes in a face-centered cubic structure.