The activation energy of a certain reaction is 46.6 kj/mol. At 20 degrees Celsius the rate constant is #0.0130s^-1#. At what temperature would this reaction go twice as fast (T2)?
1 Answer
At
Explanation:
We can use The Arrhenius Equation:
A more usable form of the equation is obtained by taking natural logs of both sides
If the reaction occurs at two temperatures
Now we can subtract both sides of
Since we know that
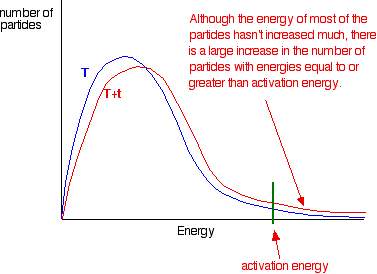
This shows how a rise of just 14 degrees can double the rate of reaction.
The graphic below shows how a small increase in temperature results in a large increase in the number of particles which have the minimum energy for a reaction to happen: