In a reaction of combustion of #H_2#, when #H_2# concentration is kept constant, the amount of #H_2# reacting increases. Explain the order of the reaction with respect to #H_2# and #O_2#?
1 Answer
Well, what this sounds like to me is that the order of the reaction depends only on
But without knowing whether the reaction is elementary or complex, that's all we can say.
If it were to be elementary, then the order would be second-order with respect to
The combustion reaction discussed is:
#2"H"_2 + "O"_2 -> 2"H"_2"O"#
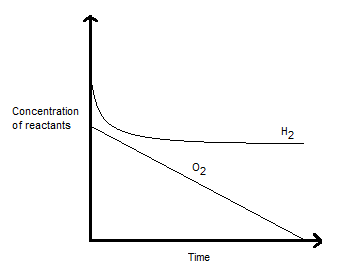
REACTION'S RESPONSE FOR H2
Based on the information given, if we keep the
That is basically like "increasing" the concentration of the reactants, which pushes the equilibrium forward as with Le Chatelier's principle.
This is reflected in more
REACTION'S RESPONSE FOR O2
As for
However, since the reactivity of
That says that the reaction rate does not depend on the concentration of
In other words, we have a rate law of:
#\mathbf(r(t)) = k_"obs"["H"_2]^m["O"_2]^0 = \mathbf(k_"obs"["H"_2]^m)#
CAVEAT: NOT KNOWING WHETHER IT'S AN ELEMENTARY OR COMPLEX REACTION
Now, without knowing the true mechanism by which this takes place, we can't really give a specific order with respect to
Basically, we can't say what
- We know whether the reaction given is an elementary or complex reaction.
- We know the exact mechanism by which the overall reaction occurs (in which case we can use the steady-state approximation on intermediate(s)).
OR...
- We have multiple trials that give enough data to determine reaction orders.
If the overall reaction were to be elementary (i.e. it literally occurs as-written), then the order would depend on the number of molecules reacting:
#color(red)(2)"H"_2 + "O"_2 -> 2"H"_2"O"# ...in which case the reaction would be second order with respect to
#"H"_2# because for every one#"O"_2# , two#"H"_2# stoichiometrically balance it.
But since we aren't told whether it is definitively an elementary reaction, all we can say is:
This reaction's order is the order with respect to
#H_2# , and the reaction is zero order with respect to#O_2# .

