Question #35861
2 Answers
Explanation:
The Average rate function is the straight line drawn between the points at each end of the interval.
So first we need to find our points,
giving us
giving us
So the gradient is equal to
rise
rise
run
run
So
This is our average rate of change between the two points.
to find the function we use,
And subbing in one of our points,
leaving us with the average rate function between
Average rate of change
Explanation:
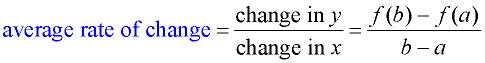
Given
Average rate of change
To find the equation :
Equation is