Consider the diagram at right, it applies to a perfectly competitive firm, which at present faces a market clearing price of $20 per unit and produces 10,000 units of output per week.?
a) What is the firm's current average revenue per unit?
b) What are the present economic profits of this firm? Is the firm maximizing economic profits?
c) If the market clearing price drops to $12.50 per unit, should this firm continue to produce in the short run if it wishes to maximize its economic profits (or minimize its economic losses)?
d) If the market clearing price drops to $7.50 per unit, should this firm continue to produce in the short run if it wishes to maximize its economic profits (or minimize its economic losses)?
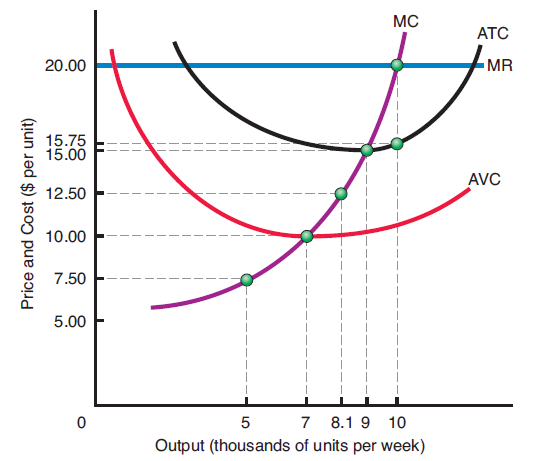
a) What is the firm's current average revenue per unit?
b) What are the present economic profits of this firm? Is the firm maximizing economic profits?
c) If the market clearing price drops to $12.50 per unit, should this firm continue to produce in the short run if it wishes to maximize its economic profits (or minimize its economic losses)?
d) If the market clearing price drops to $7.50 per unit, should this firm continue to produce in the short run if it wishes to maximize its economic profits (or minimize its economic losses)?
1 Answer
AR
Economic Profit
Explanation:
a) What is the firm's current average revenue per unit?
The firm's current average revenue per unit = $.20
For a competitive firm AR = MR = P.
b) What are the present economic profits of this firm? Is the firm maximizing economic profits?
Economic Profit
#TR = Q xx P#
#TR =10000 xx 20=$.200000#
#TC=Q xx AC#
#TC=10000 xx 15.75=157500#
Economic Profit#=200000-157500=$42500#
c) If the market clearing price drops to $12.50 per unit, should this firm continue to produce in the short run if it wishes to maximize its economic profits (or minimize its economic losses)?
The firm will continue in business, because -
The Price is higher than its AVC. It is able to cover its variable cost in full and cover a part its fixed cost.
Its minimum AVC is
Its AR is
Its minimum ATC is
d) If the market clearing price drops to $7.50 per unit, should this firm continue to produce in the short run if it wishes to maximize its economic profits (or minimize its economic losses)?
The firm will not continue to produce in the short run because it is unable to cover even its AVC.
Its AVC is
Its AR is
AR < AVC

