What is a mesure of the acidity of a compound?
2 Answers
pH. It measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution.
Explanation:
pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
The higher the concentration, the more acidic the solution.
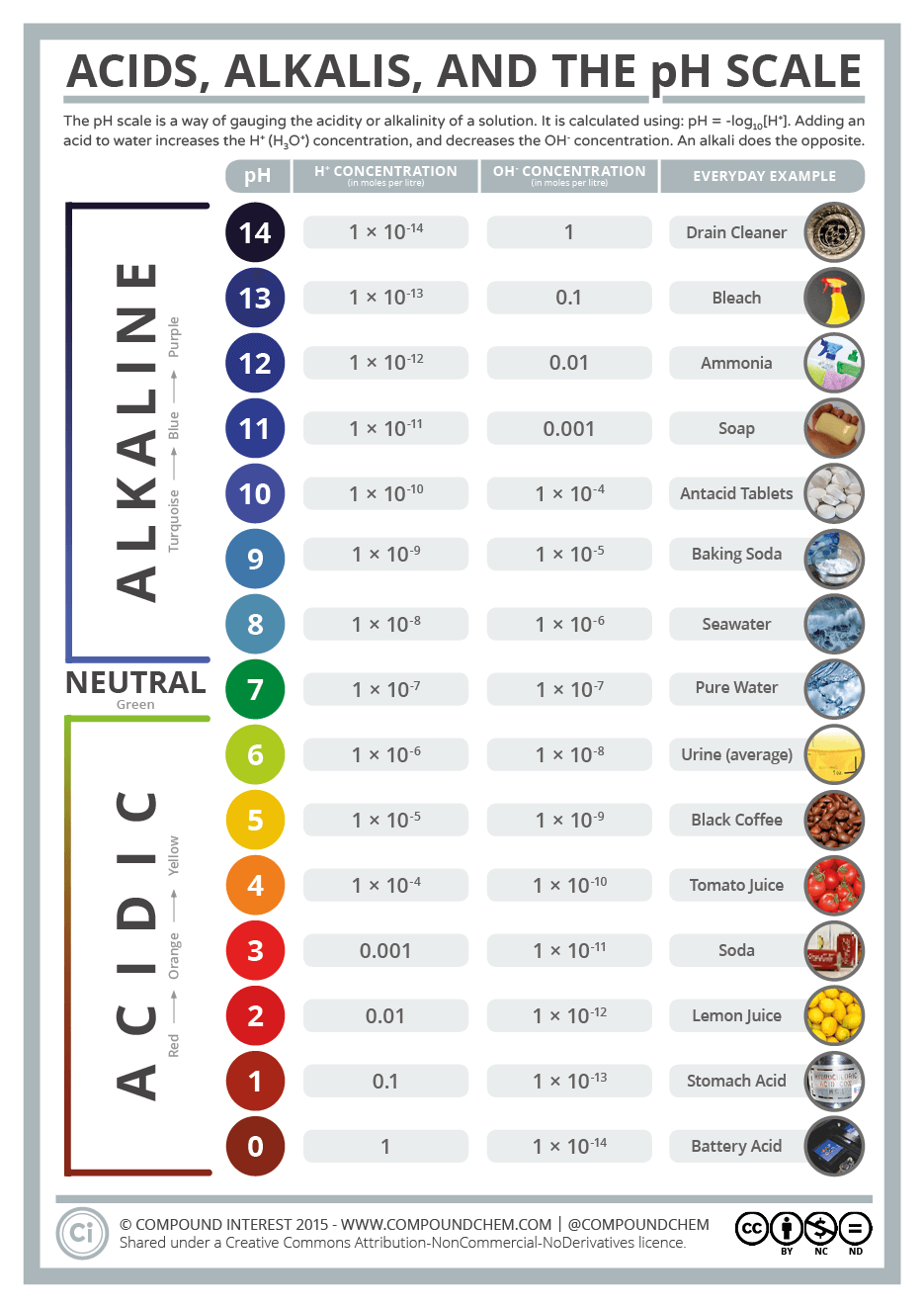
You can calculate pH by using the formula:
=> Where
=> Where
Hope this helps :)
Why, the
Explanation:
When we assess the acidity of a compound we interrogate the completion of the following equilibrium.........
As with any equilibrium, we can write the
This is an equation, that we can treat as we would any other equation.......We can take
On rearrangement..............
But by definition,
And so, finally...............
So given the


