How do electrons repel each other in multiple bonds?
1 Answer
May 24, 2017
Your premises are mistaken..........
Explanation:
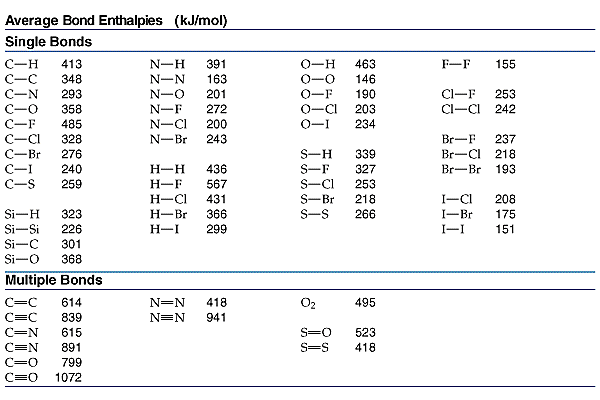
A typical
The more electrons between the carbon nuclei, the closer they can approach each other WITHOUT internuclear repulsion. And the average bond enthalpies reflect this interaction; certainly this is observed for