What is the difference between a homologous chromosome and a tetrad?
1 Answer
Tetrads are pairs of homologous chromosomes, seen in pachytene of meiosis prophase I. Homologous chromosomes do not retain the pairing otherwise.
Explanation:
Although both are very similar, the difference between the two is the pairing.
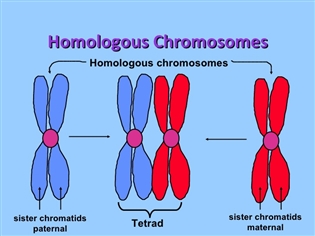
Homologous chromosomes are basically two similar chromosomes inherited from father and mother. They are homologous because they have the same genes, though not same alleles.
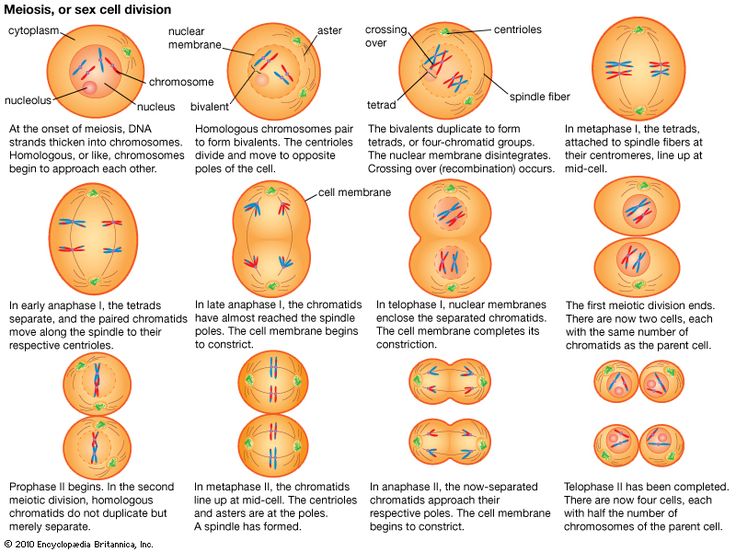
During meiosis, the homologous chromosomes pair up during first prophase. When they do so, the homologous pair becomes known as a bivalent.
Each chromosome of a bivalent undergo further coiling and sister chromatids could be distinctly seen under microscope. So each bivalent appears as 'tetrad' i.e. consisting of four chromatids.
Homologous chromosomes exchange parts in a process called crossing as the first prophase stage of meiosis continues. For this, homologous pairing and appearance of bivalent is important. Crossing over can take place when bivalent is in tetrad stage.
Hope this helps :)

( )
)

