Prove that the measure of the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two remote angles?
1 Answer
Dec 2, 2017
As proved below.
Explanation:
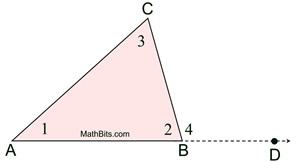
For a given triangle, sum of the three angles =
As per the diagram,
AD is a straight line and CB stands on it.
Therefore, angle 2 and angle 4 are supplementary.
I.e.
Hence
In other words, exterior angle is equal to sum of the two interior opposite (remote) angles.
Similarly, we can prove the other 5 exterior angles
