Why is carbon dioxide a non-polar molecules, even though the C−O bonds are polar?
2 Answers
Dipoles are VECTOR properties, they are summed GEOMETRICALLY.
Explanation:
For
But molecular polaity is the VECTOR sum of the individual bond dipoles, and certainly
When we go thru the same rigmarole for the water molecule, which is bent with
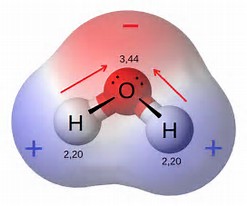 quora.com
quora.com
The numbers on the individual atoms are the electronegativities of each element.
Explanation:
If you add up the valence electrons Carbon has 4 and Oxygen has 6, but there are two Oxygens.
Because 16 is a multiple of 8, there are no lone pairs on a central Carbon atom. Carbon likes to form four bonds and because it has four valence electrons it needs four more to get to eight, so it forms four bonds. Oxygen has six valence electrons and it needs four more to get to eight, so it forms two bonds. The bonds they form are Carbon-Oxygen double bonds.
The Lewis Structure looks like this:

Oxygen is more electronegative than Carbon and the Carbon-Oxygen bond is very polar, however, if we draw the dipole moment from the partially positive Carbon atom to the partially negative Oxygen atom, you'll notice they cancel out.

This cancellation gives


