We have the following situation:
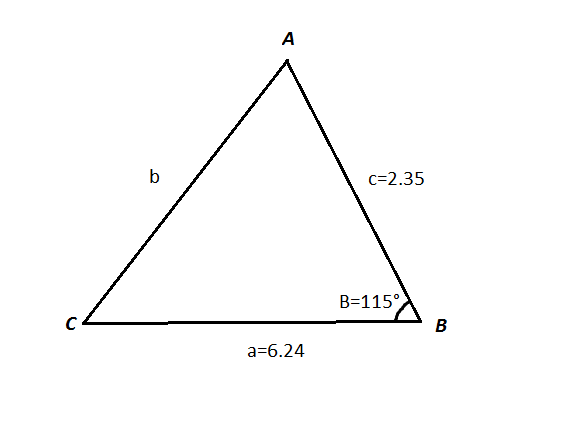
We know the sides #c#, #a# and the angle between them.
Generally, when we know this, our best bet is to apply the Law of cosines, which states that, in any triangle with sides #a# and #c# and angle between the #B#, the following relation is true:
#b^2 = a^2+c^2-2ac cos B#
This is not only true for the side #b#. In fact, we have, these are equally as true:
#c^2 = a^2+b^2-2abcosC#
#a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc cosA#
Finally, let us apply this relation in our triangle:
#b^2 = a^2+c^2-2ac cos B#
#b^2 = 2.35^2 +6.24^2 - 2*2.35*6.24*cos115°#
In order to find #cos 115°#, we can write it as #cos(45°+60°)# and apply the Sum formula for cosine:
#cos(alpha+beta) = cosalphacosbeta-sinalphasinbeta#
#:. cos115° = cos(45°+60^@) = sqrt2/2 * 1/2 - sqrt2/2 * sqrt3/2 =(sqrt2-sqrt6)/4#
To find the exact for of #b#, we should rewrite #a# and #c# as the following:
#b^2 = (235/100)^2 + (624/100)^2-2*235/100 * 624/100 * (sqrt2-sqrt6)/4#
#b^2 = 444601/10000 - 293280/10000 (sqrt2-sqrt6)/4#
#b^2 = (444601-73320sqrt2+73320sqrt6)/10000#
#color(red)(=> b=sqrt(444601-73320sqrt2+73320sqrt6)/100#


