How do you find the exact value of #sin^-1 0#?
1 Answer
Explanation:
Let's start with the unit circle:
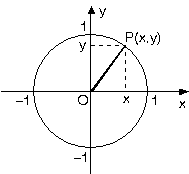
The sine ratio is the opposite divided by the hypotenuse:
What angle produces an opposite side of 0?
Let's look again at the unit circle. A triangle is formed from Point O to Point P to the x and back to Point O. The side Px is the opposite side. Right now in the diagram, that distance is certainly bigger than 0. But if we move Point P down towards the x-axis (it moves along the unit circle) the opposite side gets closer and closer to 0 until, at the angle of 0 degrees, it is 0. And that is one angle that produces a sine ratio of 0.
The other angle is on the other side of the x-axis - again, with the Point P lying on the x-axis, the opposite side = 0 and therefore the sine ratio is 0.
We're almost done. The answer isn't limited to a range of values, so the exact value is:
We can see this in the graph of sin(x):
graph{sinx [-6.28, 6.28, -1.1, 1.1]}
Remember that

