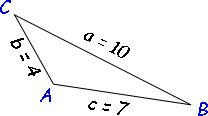First, though, here's a diagram.
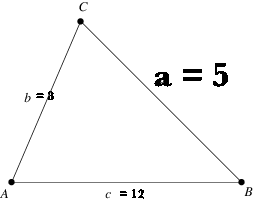
The formula for the Law of Cosine's is the following:
cosA = (b^2 + c^2 - a^2)/(2bc)cosA=b2+c2−a22bc
cosA = (8^2 + 12^2 - 5^2)/(2 xx 8 xx 12)cosA=82+122−522×8×12
cosA = 0.953125cosA=0.953125
A = cos^-1(0.953125)A=cos−1(0.953125)
A ~~ 17.61˚ or 0.39 radians
Now for angle B:
cosB = (a^2 + c^2 - b^2)/(2ac)
cosB = (5^2 + 12^2 - 8^2)/(2 xx 5 xx 12)
cosB = 0.875
B = cos^-1(0.875)
B ~~28.96˚ or 0.51 radians
Finally for angle C:
cosC = (a^2 + b^2 - c^2)/(2ab)
cosC = (5^2 + 8^2 - 12^2)/(2 xx 5 xx 8)
cosC = -0.6875
C = cos^-1(-0.6875)
C = 133.43˚ or 2.33 radians
Practice exercises:
- Solve the following triangles using the Law of Cosine's.
a)
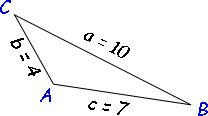
b) 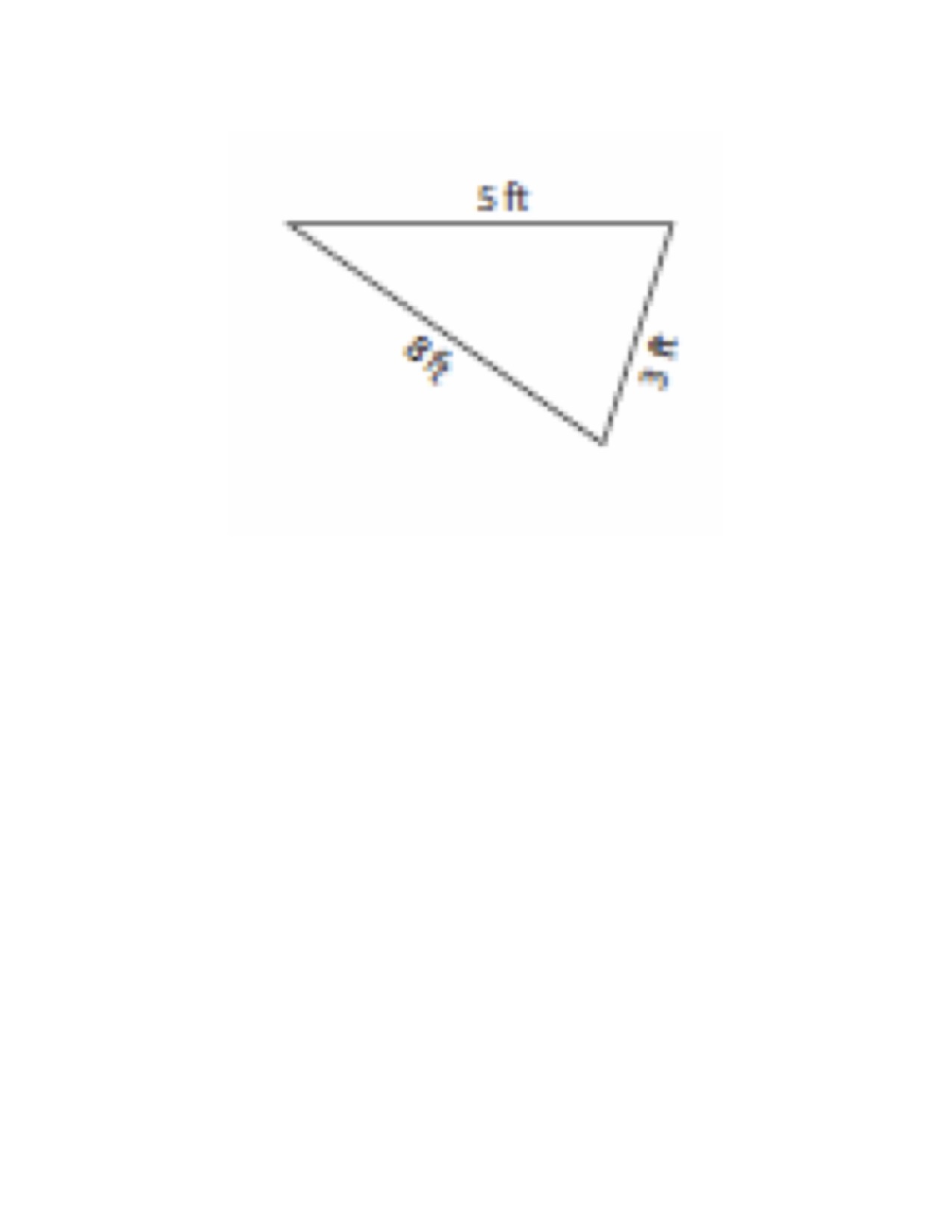
c) a = 14, b = 15, c = 16
2. We use the formula a^2 = b^2 + c^2 - (2bc xx cosA), a variation on the Law of Cosine's to find a missing side in a triangle. Use this formula to solve the following triangle:
Hopefully this helps, and good luck!