Is Williamson Ether Synthesis an SN1 or SN2 reaction?
1 Answer
Explanation:
First, it is necessary to understand the difference between an
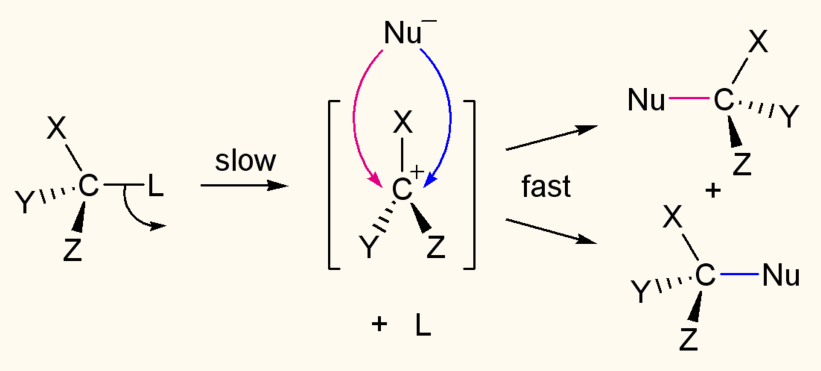
An SN1 mechanism is a two-step mechanism and racemization occurs:
- Departures of the leaving group
-> formation of carbocation -
Nucleophilic attack (usually a weak nucleophile) on carbocation
-> racemic product
An SN2 mechanism is a concerted (one-step) mechanism: -
Nucleophile attacks (strong nucleophile) from backside of leaving group
-> product has inverted stereochemistry
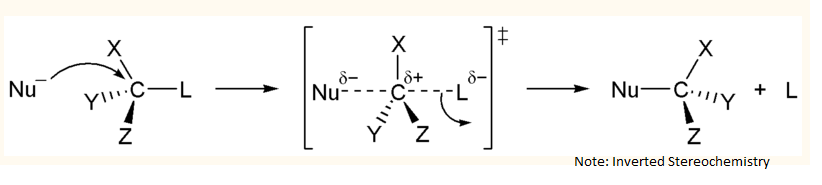
A Williamson Ether synthesis is carried out using an alcohol and an alkyl halide. First, the alcohol is deprotonated using a strong base to create an alkoxide anion as shown in the reaction below:
When the alkyl halide is added to the reaction, the alkoxide anion (
For example:
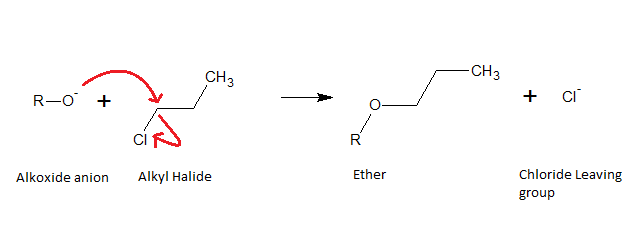
Note: The ether product will have opposite stereochemistry to the original alkyl halide at the electrophilic carbon

