Question #9d69f
1 Answer
Two atoms.
Explanation:
The idea here is that every covalent bond that
According to the octet rule, atoms are most stable when they have eight electrons in their outermost shell, which is called the valence shell.
With the exception of noble gases, which already have a complete octet, all the other atoms in the periodic table will have to form various bonds in other to obtain that stable octet configuration.
Nonmetals will form covalent bonds with each other. Covalent bonds are characterized by the fact that electrons are shared between the two atoms.
Now, a nonmetal atom can form
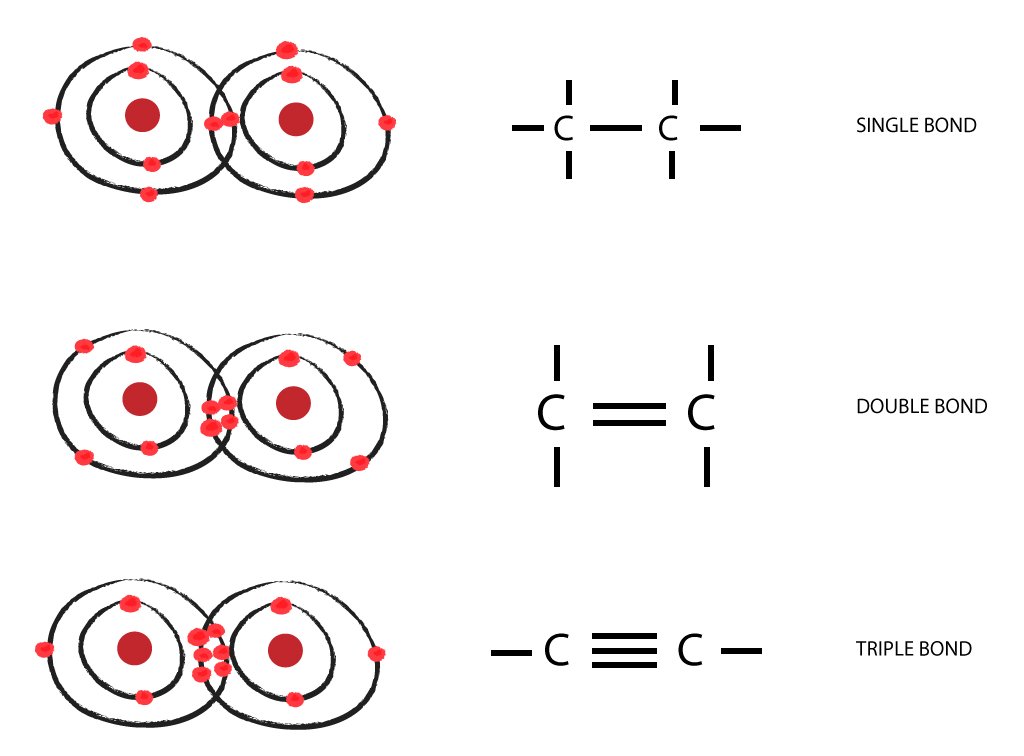
- a single bond, which consists of one sigma bond
- a double bond, which consists of one sigma and one pi bond
- a triple bond, which consists of one sigma and two pi bonds
When two atoms form a sigma or a pi bond, they're essentially sharing two valence electrons, one from each of the two atoms. This means that you will get
#"2 bonding electrons " -># a single bond#"4 bonding electrons " -># a double bond#"6 bonding electrons "-># a triple bond
You know that your atom
This double bond will thus ensure that atom
To get four more valance electrons, it can do one of two things
- form one double bond to another atom
- form two single bonds to two other atoms
Since you're looking for the maximum number of atoms that can be bonded to
This of course implies that atom
Since two electrons are being shared in a single bond, atom
Therefore, the maximum number of atoms that can bond to
This scenario corresponds to the double bond illustrated in the above image.

