Question #1628a
2 Answers
The B-I bond is weaker than the B-Br bond.
Explanation:
Because the bond between B and I is weaker, that means
Explanation:
The boron halides are Lewis acids. Their acid strength depends on their ability to accept a pair of electrons from a Lewis base.
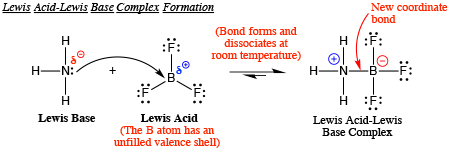
Thus, we might expect
However, it is the weakest Lewis acid of the group.
It used to be thought that the reason involved overlap between the vacant
Recent research suggests that σ bonding, not π bonding, is the important factor.
In
The
Thus, there is good
This increases the electron density on the
In
Thus, the
Since the σ electrons around
The order of acidity is


