How is backbonding treated in the theory of covalent bonding?
1 Answer
All covalent bonding is marked by the sharing of electrons between two atoms.
Explanation:
Backbonding is usually invoked in coordination chemistry, where an electron donor, a ligand, binds to, coordinates to a Lewis-acidic metal centre by donating electrons. If the metal is already in a low oxidation state, further coordination MAY not occur, unless there is a mechanism by which the metal can back-donate electron density to the ligand. Ligands such as carbon monoxide are known as
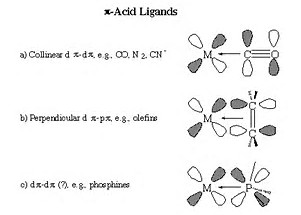
For complexes such as

