What are the different kinds of f orbitals?
2 Answers
Explanation:
So there is only one kind of
So the
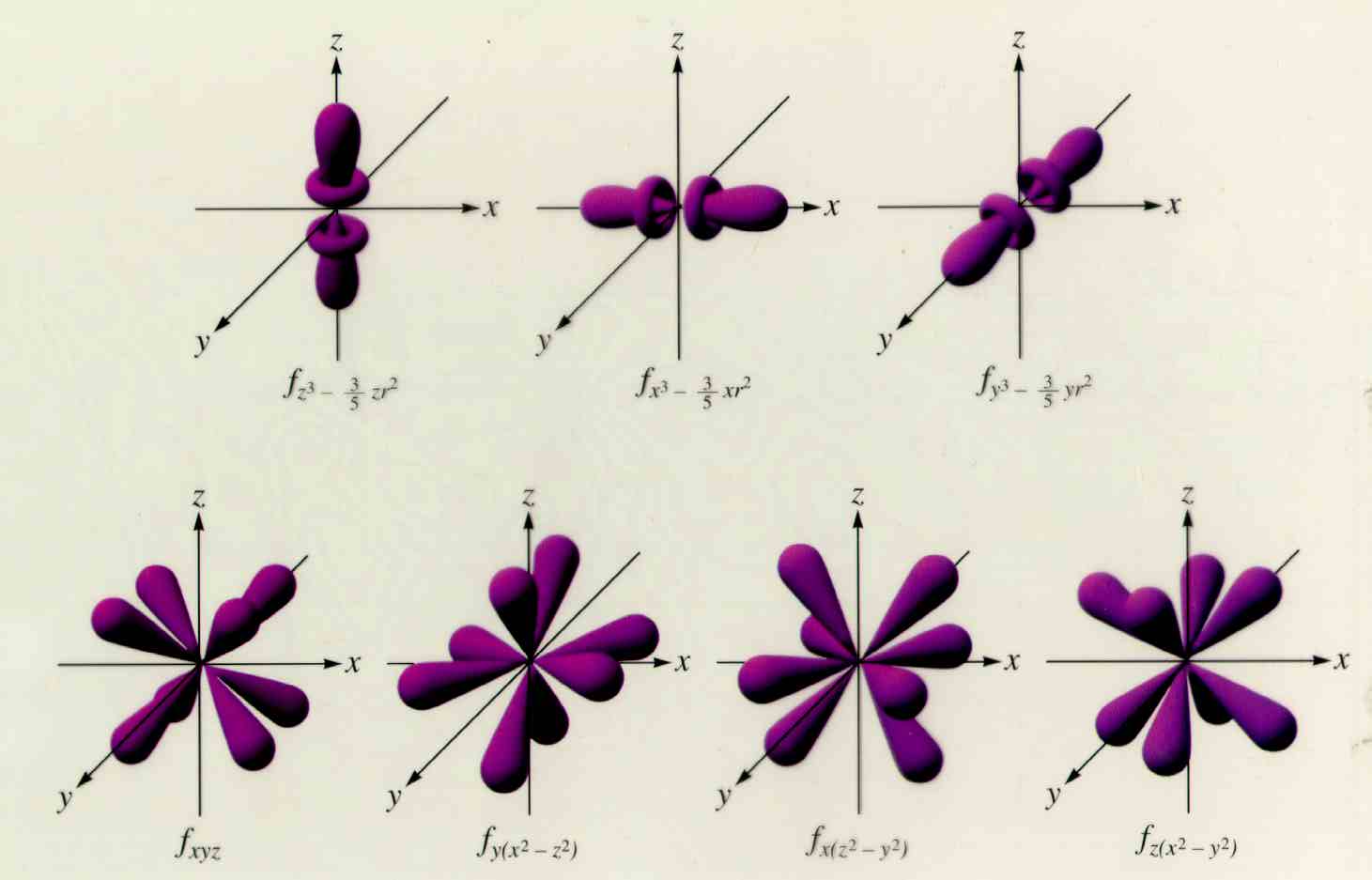
With the different dimensions. Hope it helps.
They are quite complicated, and can often do combinations of
For an introduction into these kinds of bonds:
The
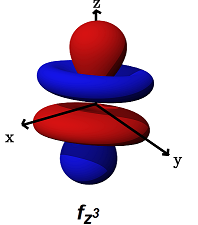
- The
#f_(z^3)# (#m_l = 0# ) is the only one that only#sigma# bonds. It can bond head-on along the#z# axis.
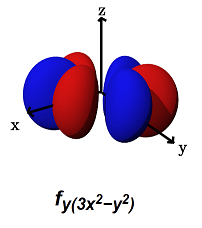
- The
#f_(y(3x^2 - y^2))# (#m_l = -3# ) can#sigma# bond along the#x# axes (for example, with a#p_y# orbital) AND#pi# bond along the#y# axes (for example, with a#p_x# orbital, or a#d_(xy)# orbital).
It can alternatively form a
#phi# bond (a six-lobed side-on overlap) along the#xy# plane (with another#f_(y(3x^2 - y^2))# orbital in a bimetallic complex).
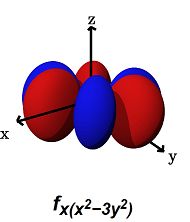
- The
#f_(x(x^2 - 3y^2))# (#m_l = +3# ) can#sigma# bond along the#y# axes (for example, with a#p_y# orbital) AND#pi# bond along the#x# axes (for example, with a#p_x# orbital, or a#d_(xy)# orbital).
It can alternatively form a
#phi# bond (a six-lobed side-on overlap) along the#xy# plane (with another#f_(x(x^2 - 3y^2))# orbital in a bimetallic complex).
- The
#f_(yz^2)# (#m_l = -1# ) can form decent#sigma# bonds along the#y# axes, AND/OR#pi# bonds along the#y# AND#z# axes.
It can alternatively form a
#phi# bond (a six-lobed side-on overlap) along the#yz# plane (with another#f_(yz^2)# orbital in a bimetallic complex).
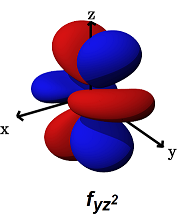
- The
#f_(xz^2)# (#m_l = +1# ) can form decent#sigma# bonds along the#x# axes, AND/OR#pi# bonds along the#x# AND#z# axes.
It can alternatively form a
#phi# bond (a six-lobed side-on overlap) along the#xz# plane (with another#f_(xz^2)# orbital in a bimetallic complex).
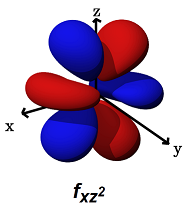
- The
#f_(z(x^2 - y^2))# (#m_l = -2# ) is for#pi# bonding along ANY of the axes,#x,y# , or#z# . The lobes lie above and below each of the axes, but also along them.
It can alternatively form a
#delta# bond with another#f_(z(x^2 - y^2))# orbital in a bimetallic complex.
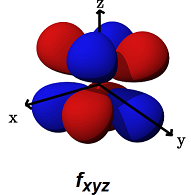
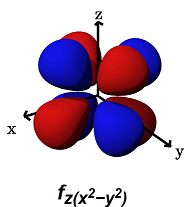
- The
#f_(xyz)# (#m_l = +2# ) is for#delta# bonding along ANY of the planes (#xz, yz, xy# ) (for example, with#d_(xy)# ,#d_(xz)# , or#d_(yz)# orbitals).
It can alternatively form a
#pi# bond with another#f_(xyz)# orbital in a bimetallic complex.



