How would you prove that the area of an equilateral triangle constructed on the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the equilateral triangles constructed on the legs?
1 Answer
Jul 23, 2018
As proved.
Explanation:
Statement of 'Pythagoras theorem': In a right triangle the area of the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares of its remaining two sides.
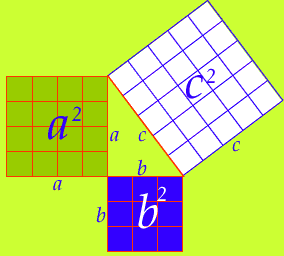
Now let's replace the a, b, c squares by equilateral triangles of sides a, b, c.
Area of equilateral triangle on hypotenuse c
Similarly,
Likewise,
